Microscopy and the Analysis of a Trichrome Stain
When imaging biological material, more often than not it is extremely difficult to differentiate between various organelles and tissues. Light scatters differently from each structure, but the change in contrast is so slight it becomes a strain to analyze the specimen. The first triple stain used to increase contrast and improve recognition dates back to 1880. One of the early methods of staining tissues for histology was developed by Claude Pierre Masson, and has since been coined the Masson trichrome stain.
Masson's trichrome stain is incredibly effective in differentiating cells and their components from the surrounding connective tissues. One of the most common stain types, which has been used on the dermal tissue sample seen in the images within this article, yields a number of colors where cell nuclei appear dark red, collagen and other tissues appear green or blue, and cell cylasm appear red/purple (Jones, 2010). These stains have been imaged under brightfield and darkfield illumination, and then again with specific filters to selectively focus on the cellular constituents of the epidermis. The primary application for the epidermal trichrome stains is differentiating healthy collagen and muscles from connective tissues onset with tumorigenesis. Typically the tumors proliferate from muscle cells and fibroblasts deep in the dermal tissue (Blitterswijk, 2010).
List of Components for Analysis of Trichrome Stain Setup | ||
|---|---|---|
Description | Stock No. | |
1. | 20X Mitutoyo Plan Apo Infinity Corrected Long WD Objective | #46-145 |
2. | MT-1 Accessory Tube Lens | #54-774 |
3. | TECHSPEC® Mitutoyo MT-1/MT-2 C-mount Adapter | #58-329 |
4. | 543nm CWL, 22nm Bandwidth, OD 6 Fluorescence Filter | #67-032 |
5. | 605nm CWL, 15nm Bandwidth, OD 6 Fluorescence Filter | #86-356 |
6. | EO-3112C ½" CMOS Color USB Camera | #59-367 |
7. | 115V, MI-150 Fiber Optic Illuminator | #59-235 |
8. | 4.25" x 3.37" Fiber Optic Backlight | #39-826 |
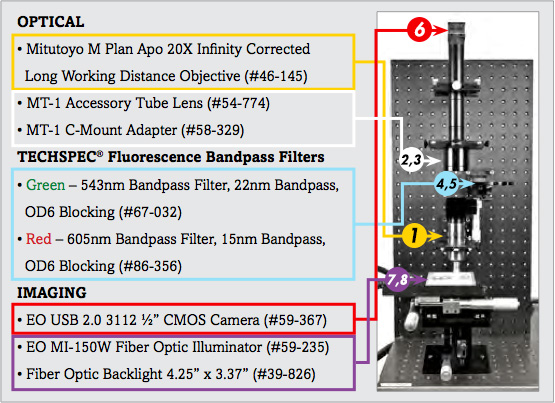
The image setup consists of a number of components, which are differentiated as optical and imaging components. The imaging products that will be discussed are the camera and illumination, and the optical components that will be discussed include the microscope objective lens and optical filters.
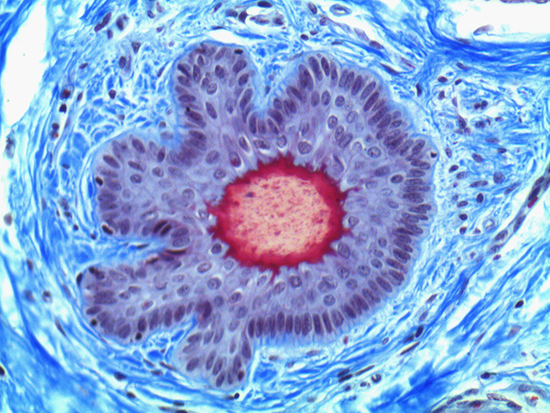
Figure 1: Brightfield Image of Dermal Tissue

Figure 2: Darkfield Imaging of Dermal Tissue
When comparing Figures 1 and 2, the visual differences are significant. A brightfield image is formed with the illumination source below the sample, and then transmitted light propagates through the sample to the sensor forming a bright, white background with sharp color. A darkfield image is formed by directing light at an oblique angle through the sample, forming a hollow cone of light which is collected by the objective. Darkfield illumination typically yields a dark background with sharp color, but in the case of Figure 2, the collagen and muscle fibers interfered with the light path and caused a blur of light and color. The dark background is hardly evident and only two distinct colors are visible. When analyzing histological stains, brightfield illumination is the preferred technique for lighting a sample.
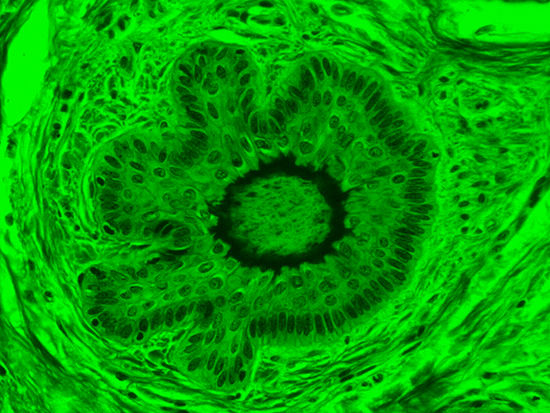
Figure 3: Brightfield Image of Dermal Tissue filtered with Green
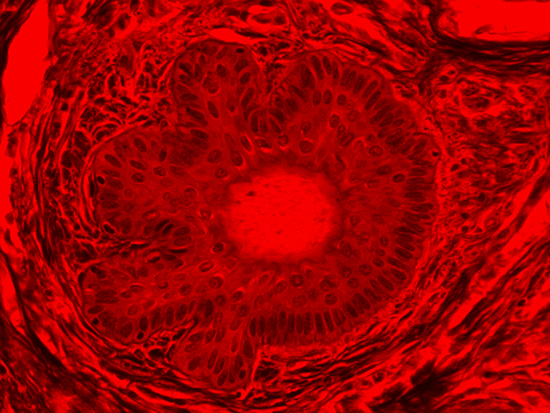
Figure 4: Brightfield Image of Dermal Tissue filtered with Red
When comparing Figure 3 with Figure 4, there is once again a significant visual difference. The most obvious feature is the change in color from green to red due to a different hardcoated filter being positioned in the optical path. The less obvious difference is the varying contrast levels caused by the filters at specific regions of the dermal tissue. For example, Figure 3 exhibits a distinct ring at the central region of the cell with additional matter within. In Figure 4, the ring is extremely faint and the internal matter is not visible. With that said, the cell and surrounding dense materials are more evident in Figure 3, whereas the muscle fibers and collagen are more pronounced in Figure 4.
Researchers have discovered a number of methods to quickly and accuray diagnose many ailments, such as many forms of cancer. As technologies continue to advance at an increasing rate, the cost of histology analysis will continue to decrease as images and videos can be easily transmitted across the globe. Even with constantly changing technology, the trichrome stain is still one of the most powerful techniques available in the field of histology and diagnostics over 100 years later.
Microscopy and the Analysis of a Trichrome Stain
When imaging biological material, more often than not it is extremely difficult to differentiate between various organelles and tissues. Light scatters differently from each structure, but the change in contrast is so slight it becomes a strain to analyze the specimen. The first triple stain used to increase contrast and improve recognition dates back to 1880. One of the early methods of staining tissues for histology was developed by Claude Pierre Masson, and has since been coined the Masson trichrome stain.
Masson's trichrome stain is incredibly effective in differentiating cells and their components from the surrounding connective tissues. One of the most common stain types, which has been used on the dermal tissue sample seen in the images within this article, yields a number of colors where cell nuclei appear dark red, collagen and other tissues appear green or blue, and cell cylasm appear red/purple (Jones, 2010). These stains have been imaged under brightfield and darkfield illumination, and then again with specific filters to selectively focus on the cellular constituents of the epidermis. The primary application for the epidermal trichrome stains is differentiating healthy collagen and muscles from connective tissues onset with tumorigenesis. Typically the tumors proliferate from muscle cells and fibroblasts deep in the dermal tissue (Blitterswijk, 2010).
List of Components for Analysis of Trichrome Stain Setup | ||
|---|---|---|
| Description | Stock No. |
1. | 20X Mitutoyo Plan Apo Infinity Corrected Long WD Objective | #46-145 |
2. | MT-1 Accessory Tube Lens | #54-774 |
3. | TECHSPEC® Mitutoyo MT-1/MT-2 C-mount Adapter | #58-329 |
4. | 543nm CWL, 22nm Bandwidth, OD 6 Fluorescence Filter | #67-032 |
5. | 605nm CWL, 15nm Bandwidth, OD 6 Fluorescence Filter | #86-356 |
6. | EO-3112C ½" CMOS Color USB Camera | #59-367 |
7. | 115V, MI-150 Fiber Optic Illuminator | #59-235 |
8. | 4.25" x 3.37" Fiber Optic Backlight | #39-826 |
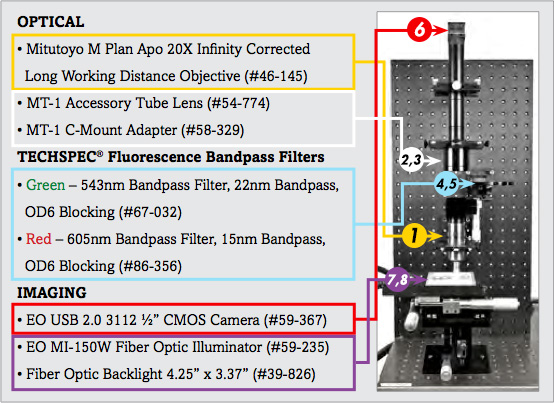
The image setup consists of a number of components, which are differentiated as optical and imaging components. The imaging products that will be discussed are the camera and illumination, and the optical components that will be discussed include the microscope objective lens and optical filters.
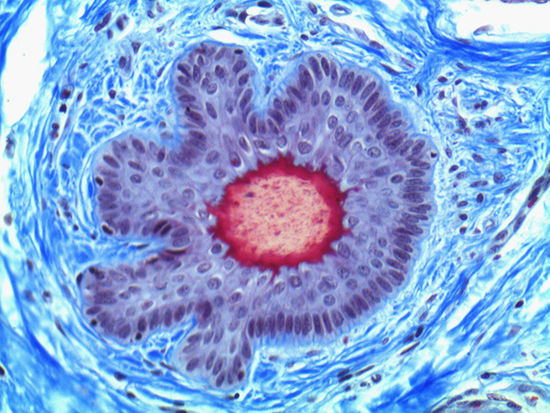
Figure 1: Brightfield Image of Dermal Tissue
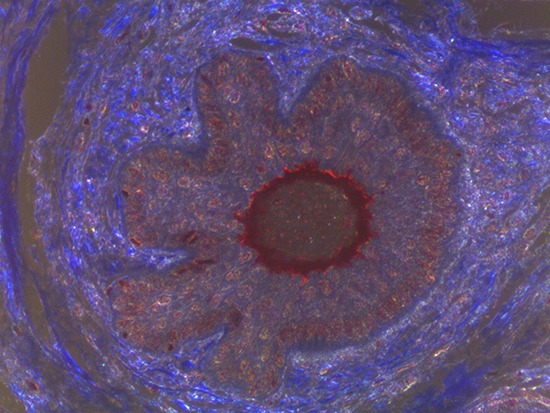
Figure 2: Darkfield Imaging of Dermal Tissue
When comparing Figures 1 and 2, the visual differences are significant. A brightfield image is formed with the illumination source below the sample, and then transmitted light propagates through the sample to the sensor forming a bright, white background with sharp color. A darkfield image is formed by directing light at an oblique angle through the sample, forming a hollow cone of light which is collected by the objective. Darkfield illumination typically yields a dark background with sharp color, but in the case of Figure 2, the collagen and muscle fibers interfered with the light path and caused a blur of light and color. The dark background is hardly evident and only two distinct colors are visible. When analyzing histological stains, brightfield illumination is the preferred technique for lighting a sample.
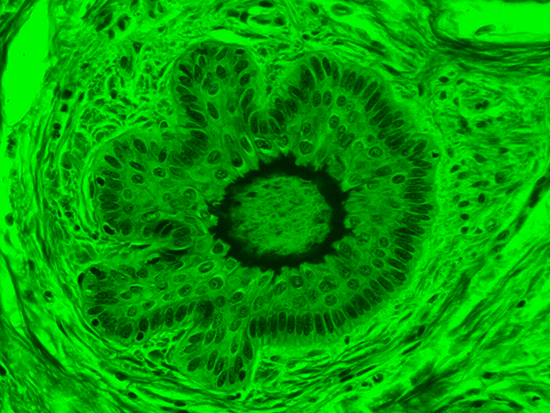
Figure 3: Brightfield Image of Dermal Tissue filtered with Green
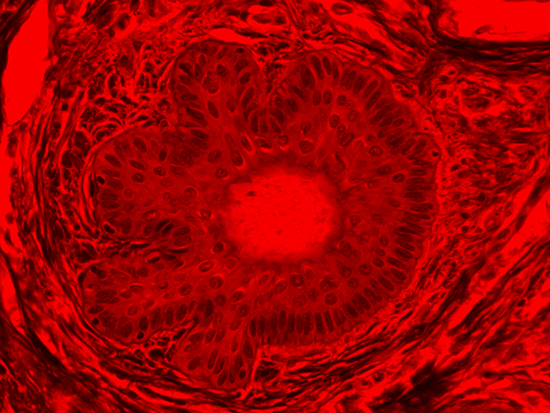
Figure 4: Brightfield Image of Dermal Tissue filtered with Red
When comparing Figure 3 with Figure 4, there is once again a significant visual difference. The most obvious feature is the change in color from green to red due to a different hardcoated filter being positioned in the optical path. The less obvious difference is the varying contrast levels caused by the filters at specific regions of the dermal tissue. For example, Figure 3 exhibits a distinct ring at the central region of the cell with additional matter within. In Figure 4, the ring is extremely faint and the internal matter is not visible. With that said, the cell and surrounding dense materials are more evident in Figure 3, whereas the muscle fibers and collagen are more pronounced in Figure 4.
Researchers have discovered a number of methods to quickly and accuray diagnose many ailments, such as many forms of cancer. As technologies continue to advance at an increasing rate, the cost of histology analysis will continue to decrease as images and videos can be easily transmitted across the globe. Even with constantly changing technology, the trichrome stain is still one of the most powerful techniques available in the field of histology and diagnostics over 100 years later.
版權(quán)所有 © 2025 江陰韻翔光電技術(shù)有限公司 備案號:蘇ICP備16003332號-1 技術(shù)支持:化工儀器網(wǎng) 管理登陸 GoogleSitemap